Colour Perception
Colour Perception
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_vision
Physiology
- Light sensitivity
- Seeing Purple (source: https://www.quora.com/Why-does-purple-light-appear-blue-in-cameras/answer/Bill-Otto-5))
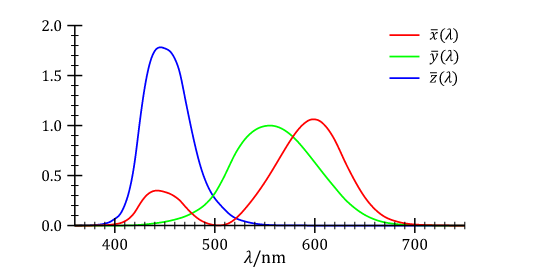
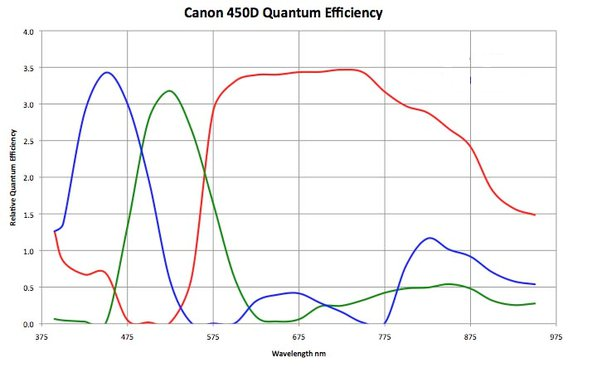
- Human Eye Quantum Efficiency (see how cones percieve some blue light as red):
- Normal Quantum Efficiency:

- Canon D450 Quantum Efficiency:
- Rod and Cone Cells
- Cone Cells
- Are three types - Short (S), Medium (M), Long (L)
- Gives colour vision
- Most are sensitive to 555 nm (Green)
- Rod Cells
- Gives low-light vision at 500 nm
- Cone Cells
Mathematics
- Physical color is a combination of pure spectral colours (in the visible range)
- Hilbert Space \(H_{colour}\) (Infinite Dimensional Vector Space) holds all colours
- Euclidian Spaces
- Each element \(C\) of \(H_{colour}\) is a function that gives an interval of all the colours \([W_{min}, W_{max}]\) to real numbers \(w\)
- So human percievable colours can be modelled by 3 numbers, to the extend to which each cone cell - S,M,L is stimulated by a wavelength \(w\) as \(s(w)\), \(m(w)\) and \(l(w)\).
- This can be thought of as points in a 3-dimensional Euclidian Space, and we call this the \({R^3}_{colour}\)